

Journal of Pharmaceutical Research
DOI: 10.18579/jopcr/v20i4.MS21083
Year: 2021, Volume: 20, Issue: 4, Pages: 58-66
Original Article
Alwaleed Yousef Aldhobaib 1, Syed Imam Rabbani ✉ 2, Mugahid A Mobark 3
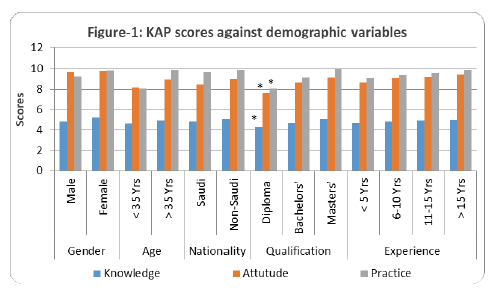
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA) is a newer class of drugs used in the treatment of adult type-2 diabetes mellitus. The use of the drugs needs appropriate methods of administration including precautions and carry some potential risks such as pancreatitis and thyroid cell neoplasia. In this cross-sectional study, a pre-validated questionnaire with fixed-answers was used to assess the medical practitioner’s response towards recently approved drugs. Their replies were recorded in an excel sheet. The data was subjected to statistical analysis using one-way ANOVA and post-hoc tests to determine the significant value. p<0.05 was used to indicate the significance of the results. The data from the study indicated that 107 health care professionals such as physicians, nurses and pharmacists with differences in age, gender, nationality, qualification and experience took part in the survey. The overall correct response to the questions of knowledge domain was found to be 73.5%, attitude – 78.5% and practice – 80.3%. However, some critical information about the method of administration, precautions and possible risks associated with the therapy is lacking among the participants. A significant variation (P<0.05) was found for some of the demographic variables such as profession, qualification and age of the participants. The finding from the study suggests that the medical professionals have good knowledge, better attitude and proper practice about the GLP-1RA that is being approved for the treatment of type-2 diabetes mellitus. However, some of the vital aspects of the medication need update. Continuing medical education programs could be one of the most suitable strategies suggested for enlightening the information on the recent additions to the therapy.
Keywords
Knowledge, Attitude, Practice, Medical professionals, Type2 diabetes, GLP1RA
© 2021 Published by Krupanidhi Educational Trust. This is an open-access article under the CC BY license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.