

Journal of Pharmaceutical Research
DOI: 10.18579/jopcr/v22.2.23.10
Year: 2023, Volume: 22, Issue: 2, Pages: 69-77
Original Article
Mohabbat Ullah ✉ 1,2 , Md. Sohel Rana 1 , Md. Monjil Hossain 3,2
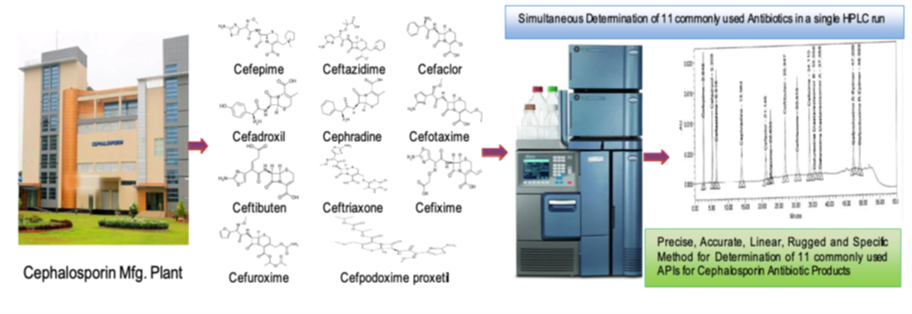
11 commonly used Cephalosporin drugs from 1st, 2nd & 3rd Generation in wastewater from Cephalosporin Antibiotics Manufacturing plant is developed, validated and proposed for routine analysis of wastewater collected from waste water pre-treatment plant (wwptp). The determined residues included the routinely manufactured cephalosporin drugs for the treatment as β-Lactams Antibiotic drugs like Cefepime, Cefadroxil, Ceftazidime, Cephradine, Cefaclor, Cefotaxime, Ceftibuten, Ceftriaxone, Cefixime, Cefuroxime Axetil and Cefpodoxime proxetil. A gradient program was developed with Xterra RP-18 (250 cm x 4.6 mm, 5 µm) column as stationary phase. All cephalosporin molecules were selective and separated with a 0.2 M Tetra-butyl Ammonium Hydroxide (TBAH) buffer and Acetonitrile in the ratio of 85:15 V/V (Solution-A) and 25:75 V/V (Solution-B), pH 6.8 was adjusted with O-phosphoric acid into the buffer solution as the mobile phase at flow of 1.2 mL min- 1 with a UV detection at 254 nm using DAD. All peaks eluted within 60 minutes gradient run. The system suitability parameters such as theoretical plate count, tailing and resolution between the closest peaks were within the limit. The method was validated following all criteria regarding ICH (Q2) guidelines. Calibrations were linear over the concentration range of 0.5–150 µg mL-1 as indicated by correlation coefficient (r) of 0.999. The developed method can be the tool for determining the Cephalosporins residue as routine quantitative analysis of waste water discharged from the Antibiotic manufacturing plant.
Keywords: Cephalosporins, Waste water, Method validation, Antibiotic Resistance, Antibiotic manufacturing plant
© 2023 Published by Krupanidhi College of Pharmacy. This is an open-access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.