

Journal of Pharmaceutical Research
DOI: 10.18579/jopcr/v18.4.tareq
Year: 2019, Volume: 18, Issue: 4, Pages: 6-11
Original Article
Tareq1, Amit Kumar Das1
1Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Krupanidhi College of Pharmacy, Bangalore, 560035, Karnataka, India
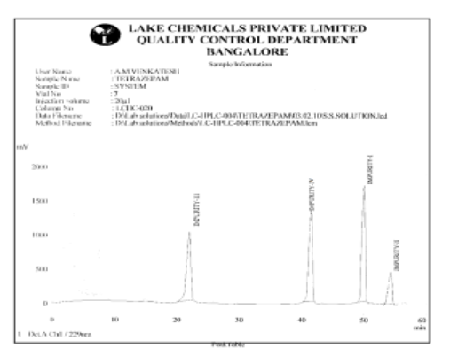
Analogues of tetrazepam, a 1,4-benzodiazepine derivative, offer potential improvements in therapeutic profiles, including enhanced efficacy, reduced side effects, and better pharmacokinetics. This study aimed to synthesize tetrazepam and its structurally related compounds, characterize and quantify their impurities, and optimize the synthesis process to improve the impurity profile, ultimately enhancing safety and reducing toxicity in drug therapy. Tetrazepam was synthesized through the reaction of anthranilic acid with sulfuryl chloride, followed by a Grignard reaction, hydrolysis, and cyclization. Structurally related impurities were generated by modifying these steps and characterized using TLC, IR, NMR, and mass spectrometry. An HPLC method with acetonitrile and potassium dihydrogen phosphate effectively separated tetrazepam from its related compounds. The yields of tetrazepam and its related compounds ranged from 68% to 95%. Structural confirmation was achieved using TLC, IR, NMR, and mass spectrometry. Tetrazepam yielded 74.82% with an Rf of 0.34 and Rt of 33.56 minutes. The impurities (IMP I–IV) had yields between 68.18% and 95.23%, with Rf values of 0.40–0.65 and Rt values of 22.52–54.35 minutes, confirming their identities. A novel approach was developed to synthesize tetrazepam and its related impurities, achieving improved purity and reduced toxicity. A new HPLC method was created to separate and identify these impurities, showing enhanced resolution and peak symmetry. This advancement significantly contributed to medicinal chemistry by providing a more refined process for analyzing benzodiazepine derivatives.
Keywords: 1,4-benzodiazepine; Tetrazepam; HPLC; TLC; IR spectroscopy; ¹H-NMR
© 2019 Published by Krupanidhi College of Pharmacy. This is an open-access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.