

Journal of Pharmaceutical Research
DOI: 10.18579/jopcr/v20i4.kishore
Year: 2021, Volume: 20, Issue: 4, Pages: 80-87
Original Article
V Kishor Kumar ✉ 1, K G Lalitha 2, R Sambath Kumar 3
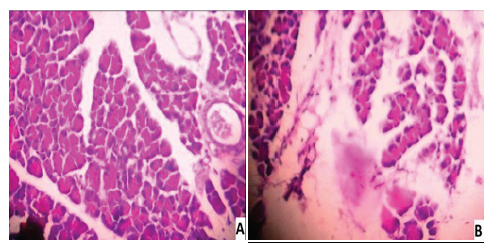
Background: Calamus rotang L (Asteraceae), also known as Pirampu in India, has long been employed in Ayurvedic medicinal formulations. It has been used to cure diabetes in folklore medicine for centuries. Aim: This Study evaluated the antidiabetic and antihyperlipidemic effects of Calamus rotang L leaves in streptozotocin-nicotinamide (STZ-NC) induced diabetic model. Methods: Estimation of fasting blood glucose, glycosylated haemoglobin, total haemoglobin, lipid profiles, lipoproteins, hepatic marker enzyme activity, and pancreas histopathology was performed in STZ-NC induced diabetic rats after receiving ethanol extract of C. rotang L leaves (100 & 200 mg/kg) for 28 days orally. The data were statistically analysed using one-way analysis (ANOVA) and post hoc multiple comparison tests. Results: The ethanol extract of C. rotang L leaves was given at doses of 100 and 200 mg/kg showed a substantial drop in fasting blood glucose levels and an increase in body weight. HbA1C, TC, TG, LDL, VLDL, AST, ALT, and ALP levels were dramatically lowered by the ethanol extract of the leaves of C. rotang L, whereas Hb, HDL cholesterol levels were significantly increased. Furthermore, in STZ-NC induced diabetes, the C. rotang L leaves ethanol extract has a positive impact on pancreas histological alterations. Conclusions: For the first time, these findings show that the C. rotang L leaves ethanol extract has significant antidiabetic and antihyperlipidemic potential, bolstering the plant's claimed application in the treatment of diabetes and its complications.
Keywords
Calamus rotang L leaves, Antidiabetic, Antihyperlipidemic, Glibenclamide
© 2021 Published by Krupanidhi Educational Trust. This is an open-access article under the CC BY license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.