

Journal of Pharmaceutical Research
Year: 2025, Volume: 24, Issue: 2, Pages: 104–109
Original Article
Pradyumna Goswami1,∗
1Assistant Professor (Chemistry), Government Ayurvedic College, Guwahati, 781014, Assam, India
*Corresponding Author
Email: pg.chem4u@gmail.com
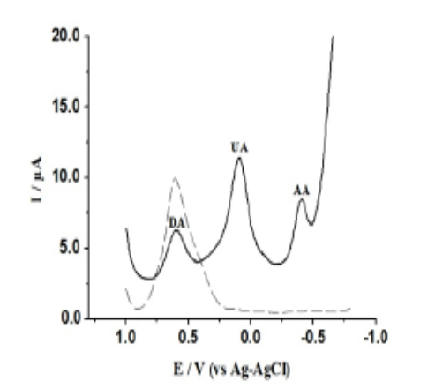
In this work sodium montmorillonite clay (NaMMT) was organomodified with cationic surfactant molecule Cetyltrimethyl Ammonium Bromide (CTAB) and 4-Nitroaniline (4NA). Glassy carbon electrode (GCE) surface was now modified with that organomodified clay. The new electrode can now be designated as 4NACME. We demonstrated determination of Dopamine (DA) and Uric Acid (UA) in presence of high concentration of Ascorbic Acid (AA) in PBS of pH 7.4 using 4NACME. Modification of GCE offers substantial improvements in voltammetric sensitivity and selectivity towards the determination of DA and UA. It can inhibit the voltammetric response of AA while the redox reaction of DA is promoted. When a square wave voltammetric (SWV) technique was used, the peak separation between DAs and AAs was found to be 979 mV and between UAs and AAs was found to be 435mV. These results were again confirmed by cyclic voltammetric (CV) technique to establish the electrochemical reversibility of DA, UA and AA at 4NACME. From linear calibration plots the slopes (µA/nM) and correlation coefficients are found to be 0.0043, 0.0041, 0.0009 and 0.9786, 0.9765, 0.9909 for DA, UA and AA respectively. The detection limits (3σ) are 8nM, 14nM and 18nM for DA, UA and AA respectively. The modified electrode showed very good reproducibility with relative standard deviation < 3%.
Keywords: Montmorillonite, Electrochemistry, Sensing, Dopamine, Uric acid, Ascorbic acid
© 2025 Published by Krupanidhi College of Pharmacy. This is an open-access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.