

Journal of Pharmaceutical Research
Year: 2024, Volume: 23, Issue: 2, Pages: 68-70
Original Article
Thomas Kurian1,∗
1Associate Professor, College of Pharmacy, Govt. T D Medical College, Alappuzha, Kerala, India
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
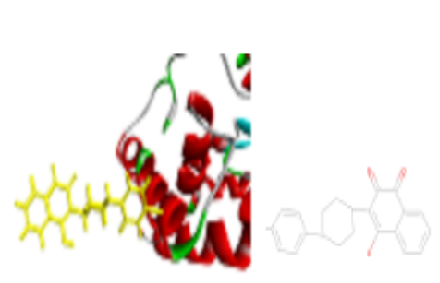
Discover new antifungal drugs by evaluating the efficacy of heterocyclic compounds. Investigate the potential of yeast Sec14p protein as a target for antifungal drugs. Compare the effectiveness of Auto Dock and PyRX software for docking simulations of heterocyclic compounds against Sec14p. Docking simulations were performed using Auto Dock and PyRX software to assess the binding affinity of five specific heterocyclic compounds to the yeast Sec14p protein. The reference compound for comparison was a known antifungal agent with a Picolamide scaffold (PDB ID: 6FOE). Atovaquone exhibited the strongest binding affinity (-9.4 kcal/mol) using PyRX. A known antifungal agent showed a significant discrepancy in binding energy between Auto Dock (-6.2 kcal/mol) and PyRX (-3.64 kcal/mol). This study explores a novel class of compounds (Quinones) for antifungal drug discovery. It highlights the potential of yeast Sec14p protein as a target for antifungal drugs. The findings suggest that PyRX might be more suitable for docking simulations of certain compound classes than Auto Dock. This emphasizes the importance of software selection based on the specific molecules under investigation.
Keywords: Molecular docking, Quinones, Antifungal, PyRX, Auto dock
© 2024 Published by Krupanidhi College of Pharmacy. This is an open-access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.