

Journal of Pharmaceutical Research
Year: 2025, Volume: 24, Issue: 2, Pages: 98-103
Original Article
Niranjana Jeba Jeeviha1, Gabriella Sharon David2, Nita Charlotte2, Mohammed Haris3,
Aniket Kumar4,∗, Margaret Shanthi5
1Junior Resident, Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacology, Christian Medical College, Vellore, 632002, Tamil Nadu, India
22nd year MBBS Student, Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacology, Christian Medical College, Vellore, 632002, Tamil Nadu, India
3Technical Assistant, Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacology, Christian Medical College, Vellore, 632002, Tamil Nadu, India
4Associate Professor, Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacology, Christian Medical College, Vellore, 632002, Tamil Nadu, India
5Professor, Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacology, Christian Medical College, Vellore, 632002, Tamil Nadu, India
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
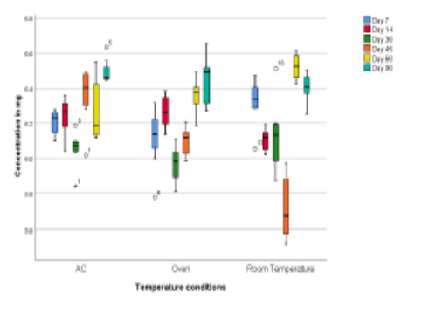
Ciprofloxacin eye drops, a topical antibiotic for ocular diseases, is commonly obtained “over the counter,” and people are not educated about the importance of storage of the medications, thus interfering with their stability. This also leads to the emergence of antibiotic resistance due to the loss of its potency. Since the room temperature in the Southern India is higher (>40°C) during summers, it is possible that there may be some amount of degradation of ciprofloxacin. Hence, the aim of the study was to estimate the effect of different storage temperatures on the potency of Ciprofloxacin at different time intervals. To evaluate the potency of 0.3% Ciprofloxacin eye drops at different storage temperatures for a period of 90 days using UV Spectrophotometer. 28 dropper bottles of 0.3% Ciprofloxacin (10 ml) were purchased from CMC Hospital pharmacy, belonging to the same batch and same brand. After randomization, 7 samples were taken as a baseline and assessed. The remaining 21 samples were divided among 3 groups (groups A, B and C) and stored at different 3 storage conditions (air-conditioned room temperature, room temperature, oven temperature), with 7 samples in each group. Concentrations of ciprofloxacin were evaluated at different time intervals at 3 different storage temperatures (25°C, 30°C, 40°C) using UV Spectrophotometer and analysed for its degradation. The 0.3% Ciprofloxacin eye drop concentration under simulated use conditions was found to be between 90% and 110% of its initial baseline value at different time intervals and three distinct storage settings.
Keywords: Ciprofloxacin, Eye-drops, Antibiotic-resistance, Stability, UV-Spectrophotometer, Fluroquinolones
© 2025 Published by Krupanidhi College of Pharmacy. This is an open-access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.