

Journal of Pharmaceutical Research
Year: 2024, Volume: 23, Issue: 1, Pages: 40-48
Original Article
N R Jadhav1,*, R B Patil2
1Department of Pharmacognosy, Prof. Ravindra Nikam College of Pharmacy Gondur, KBC NMU Jalgaon, Dhule, Maharashtra, India
2The Pharmacology Department, DCS’s A.R.A College of Pharmacy, Dhule, Maharashtra, India
*Corresponding author email: [email protected]
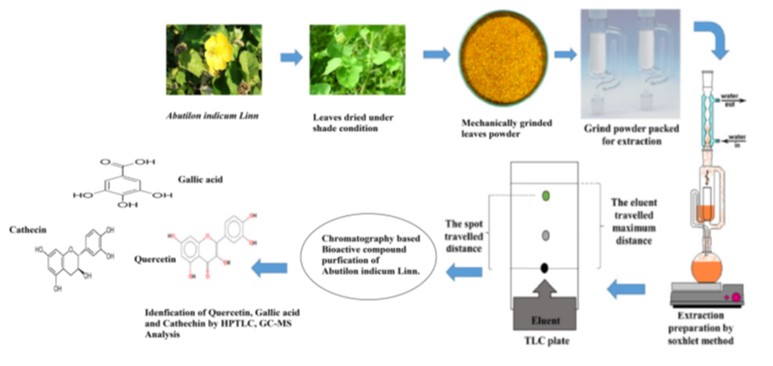
In this systematic investigation of Abutilon indicum extracts for antidiabetic activity, using TLC and HPTLC were employed to analyze bioactive compounds. The ethanolic extract (EA) exhibited specific RF values: 0.16 for catechin, 0.57 for gallic acid, and 0.70 for quercetin, with Abutilon indicum (EA) containing the highest percentages—48.87% catechin, 27.45% gallic acid, and 7.25% quercetin. The robustly developed and validated HPTLC process, applied to ethanolic extracts, demonstrated clear bands and sharp peaks, ensuring precise separation of bioactive compounds. Similar methodologies were employed for chloroform extract (CA) and aqueous extract (AA), revealing RF values of 0.10, 0.36, and 0.54 for CA, and 0.087, 0.36, and 0.53 for AA, corresponding to catechin, gallic acid, and quercetin, respectively. Fingerprinting analysis confirmed the simultaneous presence of these compounds, highlighting the method's utility for quality control. Statistical analysis supported the reliability and cost-effective suitability of HPTLC for quantitative analysis in assessing herbal material and formulations. GC-MS exploration of Abutilon indicum extracts revealed over 20 compounds in each, including flavonoids, alkaloids, and terpenoids in the ethanolic extract, and phytosterols, alkaloids, and terpenoids in the chloroform extract. The aqueous extract displayed a diverse phytochemical composition, affirming medicinal potential. These results collectively endorse Abutilon indicum's versatility and therapeutic potential in herbal medicine and pharmaceutical formulations.
Keywords
Pharmacognosy, Bioactive Compounds, Analytical Study, Abutilon indicum etc
© 2024 Published by Krupanidhi College of Pharmacy. This is an open-access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.