

Journal of Pharmaceutical Research
Year: 2024, Volume: 23, Issue: 1, Pages: 61-67
Original Article
Ajijolakewu Kamoldeen Abiodun1, Ahmed Risikat Nike1, Kazeem Muinat Olanike1, Otuyelu Frank Olakunle1,*, Abdulraheem Zulaikhat Mojisola1
1Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Life Sciences, University of Ilorin, Ilorin, Nigeria
*Corresponding author email: [email protected]
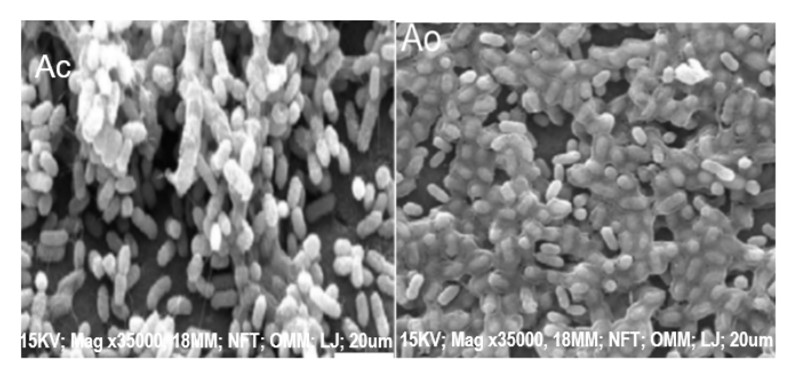
Antibacterial activity of eucalyptus essential oils (EEO) against some respiratory pathogens and its mechanism of action were studied. Clinical pathogens used in the study were Enterobacter cloacae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Disk diffusion, macro and microbroth dilution methods were respectively used to assess antibacterial assay, minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and growth inhibition assay using standard antibiotics as references. Gas chromatography Mass spectrometry was used to characterize the bioactive compounds present in EEO. Scanning electron microscopy was used to determine the mode of action of EEO on test pathogens. A total of 12 compounds were found to have bioactive functions with p-Cymene having 34.07%, gamma-Terpinene (7.01%), Cyclohexasiloxane (5.30%), 2-Aminobenzoic acid (4.59%). The EEO exerts varying antibacterial effects on susceptible organisms. At 100 mg/ml concentration the EEO antibacterial activities were observed on E. cloacae with 23.0 mm mean zone of inhibition, K. pneumoniae (22.7 mm) and S. aureus (16.0 mm) while no activity was recorded on P. aeruginosa. The MIC and MBC of the EEO on susceptible organisms were E. cloacae (6.25mg/ml, 12.5mg/ml); S. aureus (25mg/ml. 50mg/ml) respectively, while both MIC and MBC of EEO on K. pneumoniae was 50mg/ml. Scanning electron microscopy displayed noticeable damages of cell morphology and ultrastructure on two most susceptible pathogens (E. cloacae and K. pneumoniae), thus increase cell permeability and subsequent cell death. This study showed EEO is a potent antibacterials against some respiratory pathogens and can be further explored in treating respiratory and other infections caused by these pathogens. The positive effect of eucalyptus essential oil on the selected respiratory infection pathogens could make it an important part of drug (ointment formation) for the treatment of such infections.
Keywords
Essential Oils, Bioactive Compounds, Respiratory Pathogens, Susceptibility, GCMS
© 2024 Published by Krupanidhi College of Pharmacy. This is an open-access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.