

Journal of Pharmaceutical Research
Year: 2024, Volume: 23, Issue: 2, Pages: 77-82
Original Article
Hiteswar Saikia1,∗, Prabhat Ranjan Baruah2, Anju L Saikia1
1Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmacology, Assam Medical College and Hospital, Dibrugarh, Assam, India
2Associate Professor, Department of Physiology, Assam Medical College and Hospital, Dibrugarh, Assam, India
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
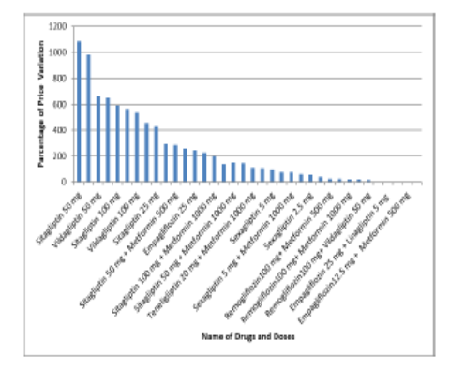
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a complex and heterogeneous group of chronic metabolic diseases causing dreaded complications increasing human sufferings, and a costly disease to manage in low/middle-income countries, which is burdensome for the most vulnerable populations, cause financial strain on individuals and family members. The purpose of the study was to analyze the price variability of different brands of sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) and dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors (DPP4i) and their combinations. The present study was an observational analytical one. The highest and lowest price of each SGLT2i and DPP4i in the same strength marketed by different pharmaceutical companies, were collected from Current Index of Medical Specialties (Jan–April 2023), Indian Drug Review (IDR 2023), Drug Today (April – July 2023) drug manuals. Calculations were done in Indian Rupees per 10 tablets/capsules. For each drug, the cost ratio and percentage of price variation (PPV) were calculated. Among DPP4i, sitagliptin 50 mg has a maximum cost ratio (5.30) and PPV (1083.66%), while sexagliptin 2.5 mg has minimal cost ratio (1.55) and PPV (55.08%). Among SGLT2i, dapagliflozin 5 mg had the highest cost ratio (10.79) and PPV (978.79%) and remogliflozin100 mg had the lowest cost ratio (1.57) and PPV (56.94%) and among combinations dapagliflozin 10 mg+ metformin 500 mg has the highest cost ratio (6.66) and PPV (565.75%), while empagliflozin 12.5 mg + metformin 500 mg has the lowest cost ratio (1.04) and PPV (4.00%). Current study shows large differences in cost ratio as well as PPV between brands. To reduce the financial burden and treatment adherence, physicians must prescribe less expensive drugs.
Keywords: Cost analysis, Cost ratio, Percentage of price variation, Diabetes mellitus
© 2024 Published by Krupanidhi College of Pharmacy. This is an open-access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.