

Journal of Pharmaceutical Research
Year: 2021, Volume: 20, Issue: 3, Pages: 38-42
Original Article
Abubakar Abdulhakim1,*, Omogbai E K Inanemo2, Nazifi A Balarabe3, Sani M Bashir1
1Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria, Nigeria
2Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, University of Benin, Benin City, Nigeria
3Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Bayero University, Kano, Nigeria
* Corresponding author email: [email protected]
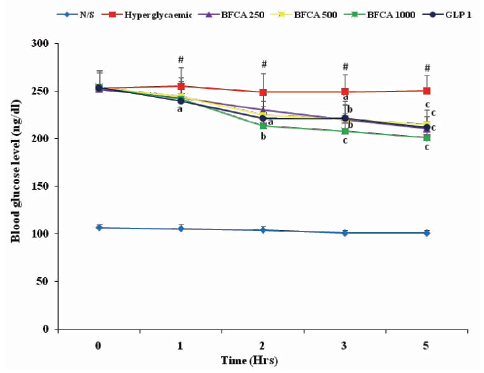
Purpose: Diabetes mellitus is a disorder associated with debilitating complications. This study was aimed at evaluating the chemical profile and antihyperglycaemic effect of butanol fraction of Chlorophytum alismifolium. Methodology: The powdered plant was extracted sequentially using soxhlet apparatus with solvents of varying polarities until butanol fraction was obtained. GC-MS analysis, phytochemical screening and acute toxicity studies were carried out. Antihyperglycaemic study was carried out using alloxan-induced hyperglycaemia in rats. Male Wistar rats were injected with 120 mg/kg of alloxan intraperitoneally, the rats with fasting blood glucose levels between 200 and 350 mg/dL were considered hyperglycaemic. Experimental groups were set up using normal rats in group I and hyperglycaemic rats in five groups of six rats each. Group II was the hyperglycaemic control while groups III, IV and V received the butanol fraction of C. alismifolium at 250, 500 and 1000 mg/kg respectively. Group VI received glimepiride 1 mg/kg. Blood glucose levels were monitored before treatment at 0 hour and 1, 2, 3 and 5 hours after treatment. Findings: Phytochemical screening revealed the presence of alkaloids, saponins, flavonoids, glycosides and triterpenes while GC-MS analysis revealed the presence of thirteen compounds some of which include; isoxazolidine, isothiazole and acetamide. Oral median lethal dose of the extract in rats was estimated to be >5,000 mg/kg. The butanol fraction of C. alismifolium at all the doses tested showed significant (p<0.05) blood glucose lowering effect when compared over time. Conclusion: The findings from this research showed that butanol fraction of Chlorophytum alismifolium possesses important compounds with antihyperglycaemic activity.
Keywords: Chlorophytum alismifolium, Hyperglycaemia, Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
© 2021 Published by Krupanidhi Educational Trust. This is an open access article under the CC BY license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.