

Journal of Pharmaceutical Research
Year: 2025, Volume: 24, Issue: 2, Pages: 89–97
Original Article
P Janeesh Das1, A Athira2, M C Jasna3, N M Hudha Fathima3, A Ameena3, Beesha S Kamal4,∗
1Department of Pharmaceuticals, National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, Chunilal Bhawan, Maniktala Main Road, Kolkata, 700054, West Bengal, India
2Department of Pharmaceuticals, National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, Guwahati, 781101, Assam, India
3College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Government Medical College, Thiruvananthapuram, 695011, Kerala, India
4College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Government T.D. Medical College, Alappuzha, 688005, Kerala, India
*Corresponding Author
Email: beeshanireesh123@gmail.com
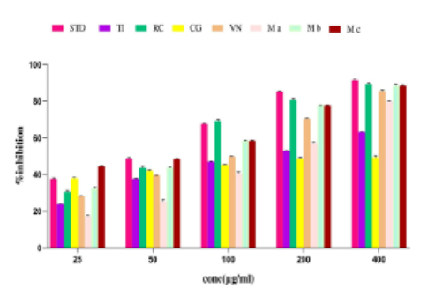
Ayurveda advocates the use of multiple herbs instead of single drugs, as their synergistic interactions lead to improved therapeutic benefits. The present study aimed to evaluate the combined antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of the ethanolic extracts of Tamarindus indica (TI), Ricinus communis (RC), Calotropis gigantea (CG) and Vitex negundo (VN), which are well known for their anti-inflammatory activity. The preliminary phytochemical screening was done, and the total phenol and flavonoid contents of the alcoholic extracts and mixtures were assessed using Folin and Ciocalteu method and aluminium chloride colourimetric method respectively. Three combinations (MX A, B and C) were developed by mixing varying quantities of the plant extracts. The antioxidant potential was screened by the in vitro DPPH radical scavenging method and the anti-inflammatory activity was evaluated by protein denaturation assay using bovine serum albumin. As a part of future evaluation, an HPTLC fingerprinting pattern using standard lupeol was also created. Phytochemical screening of all extracts showed the presence of phenolic compounds and flavonoids, which are important antioxidant and anti-inflammatory plant metabolites. All plant extracts and combinations showed good antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity that increased with concentration. RC and MX C showed maximum antioxidant activity, with IC50 values of 65.62 μg/ml and 36.45 μg/ml, respectively. MXC also exhibited good anti-inflammatory activity, with IC50 value of 28.30 μg/ml. The IC50 values of the mixtures and plant extracts were comparable to the standard quercetin and diclofenac sodium. The investigation demonstrated that various antioxidant and anti-inflammatory polyherbal formulations, utilizing the alcoholic extract of these plants should provide enhanced therapeutic activity. Moreover, the HPTLC chromatogram can serve as a valuable tool for the future assessment of formulations that include these plant mixtures.
Keyword: Polyherbal formulation; Anti-inflammatory; Antioxidant activity; Tamarindus indica; Calotropis gigantea; Vitex negundo; Ricinus communis; Lupeol
© 2025 Published by Krupanidhi College of Pharmacy. This is an open-access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.