

Journal of Pharmaceutical Research
DOI: 10.18579/jopcr/v19.2.anuradha
Year: 2020, Volume: 19, Issue: 2, Pages: 17-23
Original Article
MS Anuradha1, S Alladi1,∗
1Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Krupanidhi College of Pharmacy, Bangalore, Karnataka, India
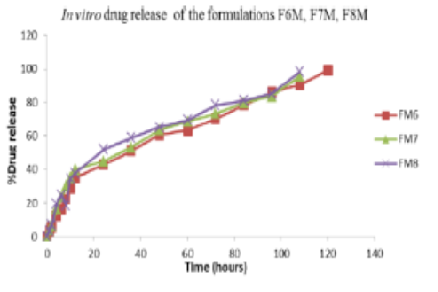
Moxifloxacin hydrochloride (Moxifloxacin HCl) is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic widely used in ocular infections. Traditional eye drops are limited by rapid drainage and low bioavailability. This study aimed to formulate stable ocular inserts that provide sustained drug release, enhance antimicrobial efficacy, ensure ocular safety, and establish a strong in vitro–in vivo correlation for predictable therapeutic performance. The λmax of Moxifloxacin HCl in distilled water and simulated tear fluid was 288.5 nm. Drug-polymer compatibility was established through Fourier Transform Infrared spectroscopy. The ocular inserts were prepared using polyvinyl alcohol as the reservoir and ethyl cellulose as the rate-controlling membrane. Physicochemical characteristics, in vitro release of drug in Franz diffusion cell, antimicrobial activity in agar diffusion test, in vivo efficacy in rabbit model, and irritation potential using the Draize test were evaluated. The release kinetics and stability of the drug were studied. Formulation FM6 exhibited uniform thickness of 0.298 ± 0.02 mm with pH 7.27 and drug content of 0.991 ± 0.06 mg. The in vitro release exhibited 99.1% drug delivery within five days with Higuchi kinetics (R2 = 0.991). FM6 exhibits severe antimicrobial activity and sterility. Sustained release and lack of ocular irritation have been established by in vivo studies. Accelerated stability tests did not show any degradation for 3 months. The current study successfully developed and optimised a new sustained-release ocular insert for Moxifloxacin HCl with extended antimicrobial activity and enhanced patient compliance.
Keywords: Moxifloxacin HCl, Ocular Insert, Sustained Release, In Vitro, In Vivo
© 2025 Published by Krupanidhi College of Pharmacy. This is an open-access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.