

Journal of Pharmaceutical Research
DOI: 10.18579/jopcr/v20.2.pradeep
Year: 2021, Volume: 20, Issue: 2, Pages: 6-10
Original Article
N Pradeep1, R M Rohini1,∗
1Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Krupanidhi College of Pharmacy, Bangalore, Karnataka, India
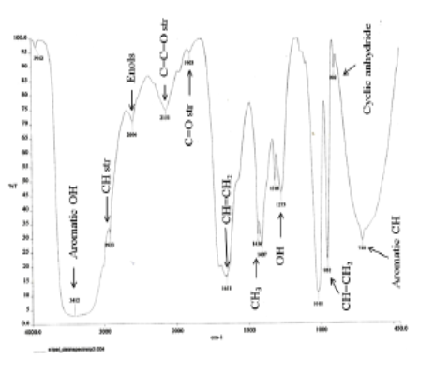
Alangium salvifolium is a medicinal plant that has been studied for its medicinal properties. This study aimed to isolate and identify bioactive molecules from A. salvifolium leaves and examine their medicinal properties. Dried leaves of A. salvifolium were extracted with petroleum ether, chloroform, and methanol using successive extraction protocols. The petroleum ether extract was then purified by column chromatography using a solvent gradient, petroleum ether, ethyl acetate, methanol, and silica gel. Isolated compound AS-01 was then analyzed by thin-layer chromatography, high-performance liquid chromatography, high-performance thin-layer chromatography, and different spectroscopic analyses, such as Fourier Transform Infrared, 1H-Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy, and mass spectrometry. AS-01 was isolated as a white crystalline compound with a molecular weight of 528 and purity of 90%, as confirmed by HPLC. The compound showed strong structural characteristics in the form of hydroxyl, methoxy, and aromatic groups. The compound was positive for alkaloids, and the retention factor (Rf) value was aligned with the standards in both TLC and HPTLC. This study reports a novel alkaloid AS-01. The isolation and structural elucidation of AS-01 revealed new insights into the pharmacological potential of the plant.
Keywords: Alangium salvifolium, Alkaloids, Isolation, Column Chromatography, Spectroscopic Analysis
© 2021 Published by Krupanidhi College of Pharmacy. This is an open-access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.