

Journal of Pharmaceutical Research
Year: 2025, Volume: 24, Issue: 2, Pages: 78-82
Original Article
Thomas Kurian1,∗, Rani Sebastian2
1Associate Professor, College of Pharmacy Govt. Medical College, Alappuzha, Kerala, India
2Assistant Professor, College of Pharmacy Govt. Medical College, Kottayam, Kerala, India
∗ Corresponding author.
Thomas Kurian
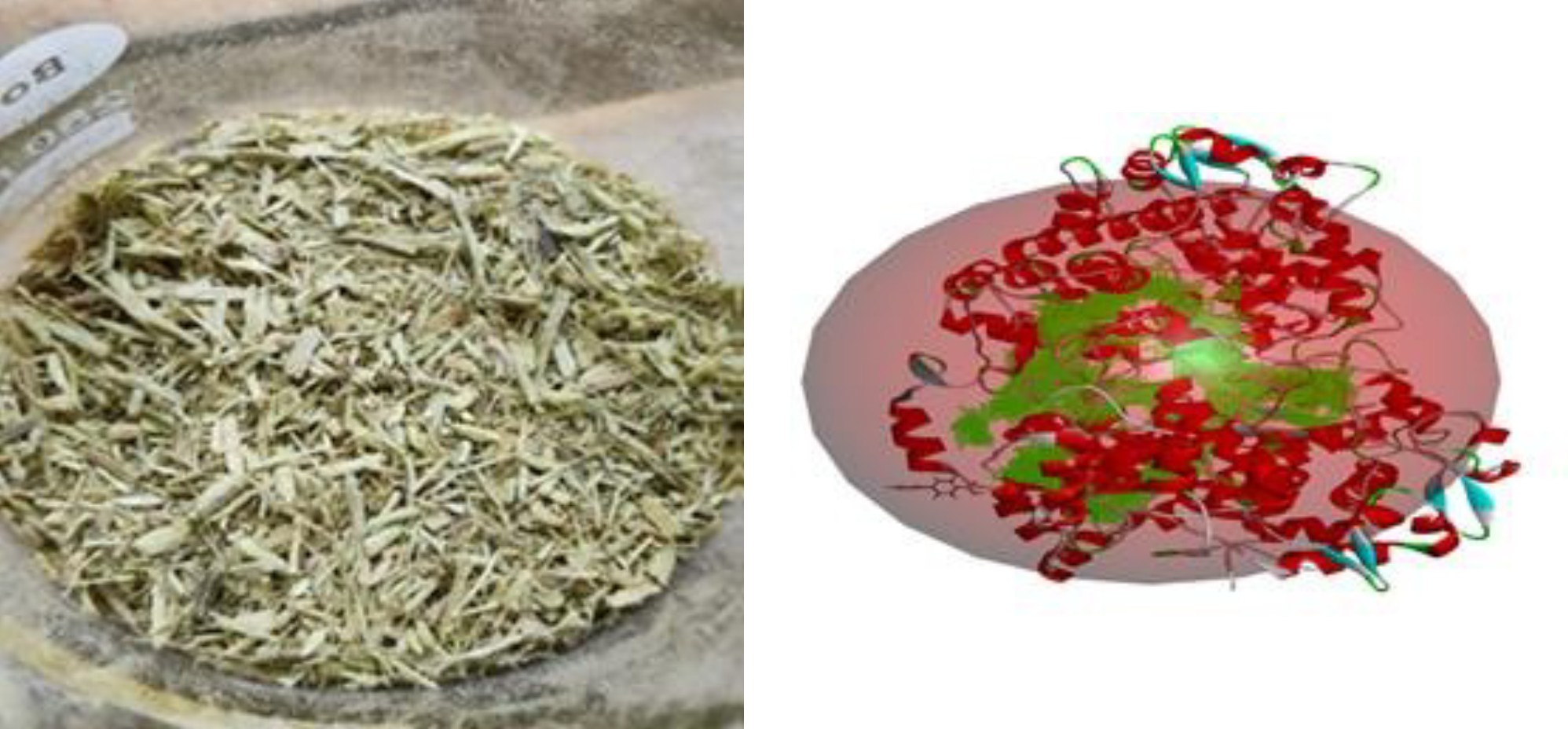
Clerodendrum thomsoniae Balf.f., Lamiaceae family has its traditional medicinal uses. This study used the molecular docking technique to examine the phytochemicals and their anti-inflammatory effect in silico. PyRX, a docking program using the Vina Wizard tool, was employed. For the investigation, the plant's Ariel parts were utilized. Soxhlet extraction using ethanol was carried out. Proteins, alkaloids, carbohydrates, flavonoids, glycosides, saponins, and tannins were all detected in the initial phytochemical analysis. The plant ethanolic extract was subjected to GCMS analytics, which revealed the presence of some significant Phyto compounds Bis (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate, 4-Biphenyl carboxylic acid, Do doxylamine, “N-(2,3,4,6 Tetra –o- acetyl beta- alpha-glucose pyrantel) glycine “which was used as ligands for docking study. The receptor used was 5KIR, Vivoxx bound to human COX-2 enzyme. PyRX docking revealed that the best active compound, 4-Biphenyl carboxylic aid, scored 7.7 compared to the standard Rofecoxib 6.7 drug docking score. Further, in-vivo, in-vitro, and clinical studies may be carried out to validate these results and for further SAR modification in drug development. The antioxidant activity established by in-vitro methods adds to the anti-inflammatory activity predicted.
Keywords: Clerodendrum; Extraction; Docking; Anti-inflammatory
© 2025 Published by Krupanidhi College of Pharmacy. This is an open-access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.