

Journal of Pharmaceutical Research
Year: 2024, Volume: 23, Issue: 4, Pages: 199-203
Review Article
Rashmi Wani1,∗, Sunny Roy2, Darsh Jain2, Shreya Menon2
1Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Vivekanand Education Society’s College of Pharmacy, Affiliated to University of Mumbai, Chembur, Mumbai, 400074, Maharashtra, India
2Student of Final Year B Pharm, Vivekanand Education Society’s College of Pharmacy, Affiliated to University of Mumbai, Chembur, Mumbai, 400074, Maharashtra, India
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
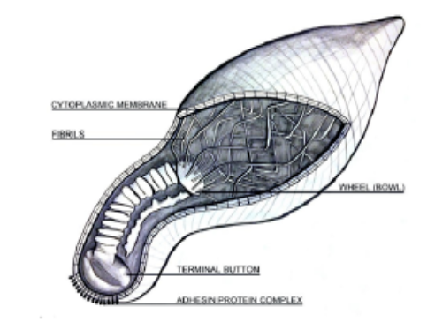
A major contributor to atypical community-acquired pneumonia, Mycoplasma pneumoniae poses a special challenge in the clinical and scientific arenas because of its unique features, which include its tiny genome size, absence of a cell wall, and capacity to elude host immune responses. The many aspects of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections, including epidemiology, etiology, clinical symptoms, and diagnostic methods, are thoroughly reviewed in this study. A critical examination of existing treatment techniques and emerging therapeutic options is presented, coupled with an exploration of the changing terrain of antibiotic resistance in strains of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Comprehensive knowledge of this sneaky pathogen is aided by insights into immune evasion mechanisms, host-pathogen interactions, and the function of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in chronic respiratory infections. This review is a useful resource for physicians, researchers, and other healthcare professionals by combining current scientific findings with clinical viewpoints.
Keywords: Mycoplasma pneumoniae; Respiratory illness; COVID-19; Epidemics
© 2024 Published by Krupanidhi College of Pharmacy. This is an open-access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.