

Journal of Pharmaceutical Research
DOI: 10.18579/jopcr/v22.3.23.59
Year: 2023, Volume: 22, Issue: 3, Pages: 124-132
Review Article
Kishor Jain1,*, Dhanshri Kachare2, Rajnigandha Gaikwad2, Mansi Kalje2, Manjusha Kantule2, Sudeshana Mohite2, Nikita Rodage2, Vikas Kandekar3, Archana Thikekar1
1Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Rajmata Jijau Shikshan Prasarak Mandal’s College of Pharmacy, Maharashtra, India
2Department of Pharmacology, Rajmata Jijau Shikshan Prasarak Mandal’s College of Pharmacy, Maharashtra, India
3Citron Life Sciences Pvt. Ltd. Ahmednagar, Maharashtra, India
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
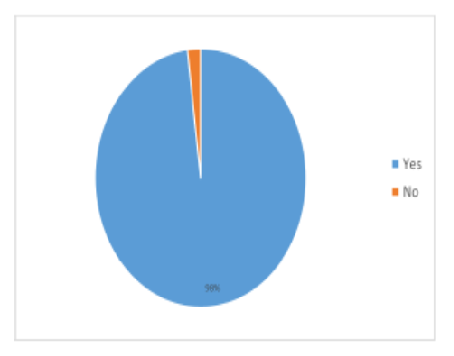
Objective: Kidney stones or nephrolithiasis, is a common problem worldwide. About 12% of the Indian population is estimated to have kidney stones and out of which 50% may end up with loss of kidney functions. In the first part of this article the pathophysiology of kidney stone, its types, risk factors, signs, symptoms, diagnosis and therapy have been discussed. Furthermore, various therapeutic approaches for kidney stone management are also briefly renewed. Methods: The second part of this article discusses a herbal formulation Ren-Cit® successfully used to treat kidney stone, its usage, composition as well as the actions of each of its medicinal constituents. A survey of patients who used Ren-Cit® has been conducted. Finding: The analysis of this survey revealed that 98% of the patients were suffering from kidney stone. Out of these 78% of the patients had hypertension and diabetes. None of the participants observed any side effects from the usage of Ren-Cit®. A total of 76% patients got relief from kidney stone by using Ren-Cit®. Various types of kidney stones diagnosed in these patients had varied composition, viz.; calcium oxalate stone (52%), calcium phosphate stone (16%), uric acid stone (12%), struvite stone (12%) and cystine stone (8%). Novelty: Ren- Cit® ayurvedic formulation proved to be effective on a wide range and types of kidney Stones.
Keywords: Kidney Stone; Urolithiasis; Calcium Oxalate; Uric Acid Stone; Calcium Phosphate; Ren-Cit®
© 2023 Published by Krupanidhi College of Pharmacy. This is an open-access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.