

Journal of Pharmaceutical Research
DOI: 10.18579/jopcr/v20i3.ms21056
Year: 2021, Volume: 20, Issue: 3, Pages: 24-29
Original Article
D Jothieswari1,*, R M Soniya1, R S Vinuthna1, P Venkatesh1, V Hari1
1Sri Venkateswara College of Pharmacy, RVS Nagar, Chittoor, 517127, Andhra Pradesh, India
*Corresponding Author Email: [email protected]
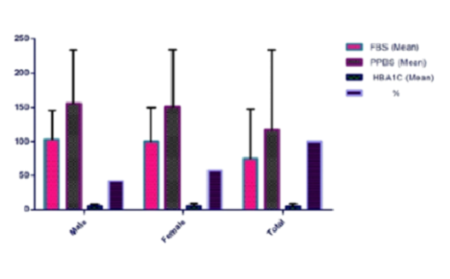
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder of heterogenous type. Diabetic complications are mostly associated with condition of vascular penetrability that affects different tissues & kidneys, retina, nerves which involve the body organs.The aim of study was to assess the prevalence of micro and macro diabetic complications and risk factors of diabetic patients. The prospective observational study was conducted in Raghu Diabetes and general clinic, Chittoor, Andhra Pradesh. A sample size of 200 subjects was recruited for the study. The study was conducted from December 2020 to May 2021. Patients with age group of 30-90 years and diabetic complications were included in the study. Patients below 30 years of age were excluded from study. The patient details were collected using questionnaire form. It contains sociodemographic data and medical history including smoking, alcohol, family history of diabetes mellitus, and treatment and management of diabetes. The statistical analysis was carried out using SPSS version 25.0. The study results showed 1.5% of patients had more than two co-morbidities, which was significantly higher among elderly (5.04%), females (5.2%) and urban residence (6.31%), physical inactivity (3.15%) and house wife (2.1%). The statins prescribed patients were 160 (80%) whereas patients on other medications, insulin in combination with OHA 38 (19%), and multivitamins prescribed patients 181 (90.5%). The study showed the patient’s age of 51- 70 years was mostly affected by diabetes. Regular exercise, intake of more vegetables and fruits and adopting a healthier life-style can reduce the prevalence of diabetes.
Keywords: Diabetic complications; physical inactivity; smoking; alcohol; statins; Insulin
© 2021 Published by Krupanidhi Educational Trust. This is an open access article under the CC BY license. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.