

Journal of Pharmaceutical Research
DOI: 10.18579/jopcr/v19.3.prathyn
Year: 2020, Volume: 19, Issue: 3, Pages: 7-11
Original Article
P Prathyun1, Mayukh Baidya1,∗
1Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Krupanidhi College of Pharmacy, Bangalore, Karnataka, India
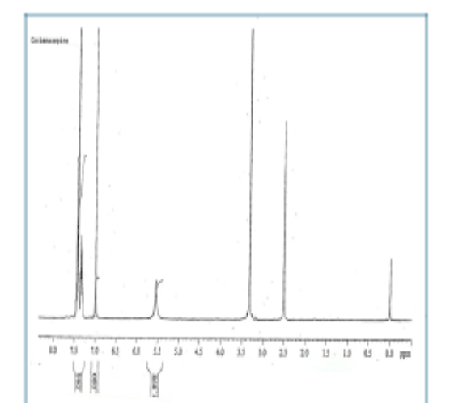
Oxcarbazepine and carbamazepine are both commonly used anticonvulsant drugs, and the identification and control of impurities are of paramount importance for product safety and efficacy. The aim of this study was to synthesise, isolate, and characterise the major process-related impurities that form during their production. Process-related impurities were synthesised through selective chemical reactions of raw materials, such as 10-methoxyiminostilbene, hydroxylamine hydrochloride, and sodium cyanate, in a controlled environment. Two reaction schemes were used to produce oximinostilbene,10-methoxycarbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, and carbamazepine. Purification was performed via solvent extraction and recrystallisation. Characterisation was performed using Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC), infrared (IR) Spectroscopy, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR), and Mass Spectrometry (MS). The synthesised process-related impurities were confirmed by physicochemical and spectroscopic methods. Oximinostilbene (73% yield), 10-methoxycarbamazepine (80%), oxcarbazepine (75%), and carbamazepine (46%) yielded clear melting points and Rf values. IR, NMR, and MS analyses confirmed the structural identity and purity of each compound. The present study provides a detailed synthesis and extensive structural elucidation of process-related impurities not only in oxcarbazepine but also in carbamazepine routes to support impurity profiling for regulatory and quality control standards.
Keywords: Oxcarbazepine, Carbamazepine, Impurities, Mass spectra
© 2020 Published by Krupanidhi College of Pharmacy. This is an open-access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.